- Article
Optimizing RTAB-Map Viewability to Reduce Cognitive Workload in VR Teleoperation: A User-Centric Approach
- Hojin Yoon,
- Haegyeom Choi and
- Donghun Lee
- + 1 author
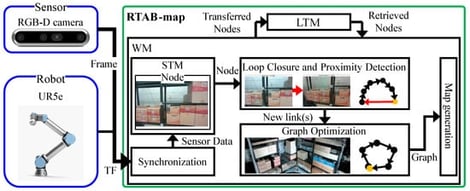
In industrial environments, providing intuitive spatial information via 3D maps is essential for maximizing the efficiency of teleoperation. However, existing SLAM algorithms generating 3D maps predominantly focus on improving robot localization accuracy, often neglecting the optimization of viewability required for human operators to clearly perceive object depth and structure in virtual environments. To address this, this study proposes a methodology to optimize the viewability of RTAB-Map-based 3D maps using the Taguchi method, aiming to enhance VR teleoperation efficiency and reduce cognitive workload. We identified eight key parameters that critically affect visual quality and utilized an L18 orthogonal array to derive an optimal combination that controls point cloud density and noise levels. Experimental results from a target object picking task demonstrated that the optimized 3D map reduced task completion time by approximately 9 s compared to the RGB image condition, achieving efficiency levels approaching those of the physical-world baseline. Furthermore, evaluations using NASA-TLX confirmed that intuitive visual feedback minimized situational awareness errors and substantially alleviated cognitive workload. This study suggests a new direction for constructing high-efficiency teleoperation interfaces from a Human–Robot Interaction perspective by expanding SLAM optimization criteria from geometric precision to user-centric visual quality.
6 February 2026